Python dictionaries are data structures that contain elements (items) formed by a key (key) and a value (value).
my_dict = {“key_1”: “value_1”, “key_2”: “value_2”, “key_3”: “value_3”, …}
Let’s see a basic example:
my_dict = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
print(my_dict)
The my_dict dictionary contains alphabetic keys and numeric values. The keys of a dictionary must be unique and can be declared to get the corresponding value.
So if for example I want to print a dictionary in Python I can write:
print (my_dict [‘a’])
If the key does not exist, a keyError is returned. To check if a key exists in Python dictionaries we can use the in or not in operator to see if it is not present.
if('a' in student):
print(my_dict['a'])
Let’s take another example of a Python dictionary that contains student data:
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
print(student)
print(student['name'])
Calculating the length of the Python dictionaries
To calculate the length of a dictionary we use the function len (d). This function calculates the number of key-value pairs contained in the dictionary.
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
print(len(student))
Operations with Python dictionaries
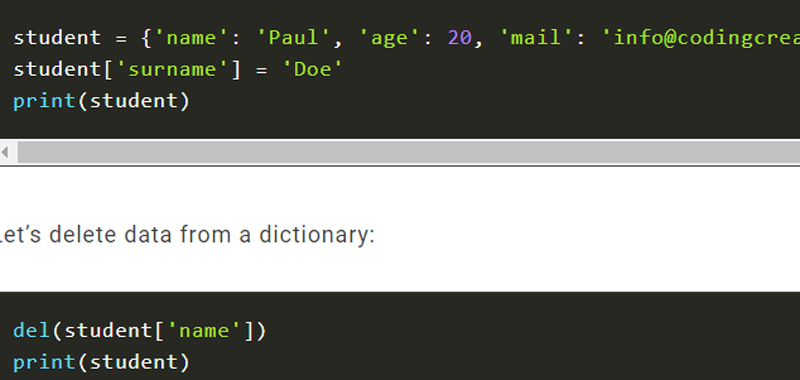
Let’s add data to a dictionary:
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
student['surname'] = 'Doe'
print(student)
Let’s delete data from a dictionary:
del(student['name'])
print(student)
Methods supported by dictionaries in Python and which we will study in detail:
| Method | Description |
| d.items() | returns all dictionary key-value pairs d |
| d.keys() | returns all dictionary keys d |
| d.values() | returns all dictionary values d |
| d.pop(key, default) | removes the value from the dictionary |
| d.popitem() | delete the last item from the dictionary |
| d.update(d2) | adds elements of a d2 dictionary to the dictionary d |
| d.copy() | creates and returns a copy of the dictionary d |
| d.clear() | empty your dictionary d |
Let’s take some examples. We use the d.items() method to display all key-value pairs, as a set of tuples:
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
print(student.items())
We use d.keys() and d.values() to display the keys and values of the dictionary d:
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
print(student.keys())
print(student.values())
We use the d.update(d2) method in Python to merge two dictionaries:
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
student_address = {'Country': 'London', 'State': 'UK', 'street': 'coding creativo'}
student.update(student_address)
print(student)
We use the d.clear() method to clear the dictionary:
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
student.clear()
print(student)
This way you get an empty dictionary!
We use the d.popitem() method to remove the last element from the dictionary:
student = {'name': 'Paul', 'age': 20, 'mail': 'info@codingcreativo.it'}
student.clear()
print(student)
There are other methods to use on dictionaries in Python which we will cover later.

[…] Prev lesson: The factorial of a number in PythonNext lesson: Introduction to dictionaries in Python […]