List in Python is an ordered series of values identified by an index.
So a list is a composite data that aggregates values of any type, enclosed in a pair of square brackets and separated by a comma.
Values that are part of a list are called elements and can be numbers or strings.
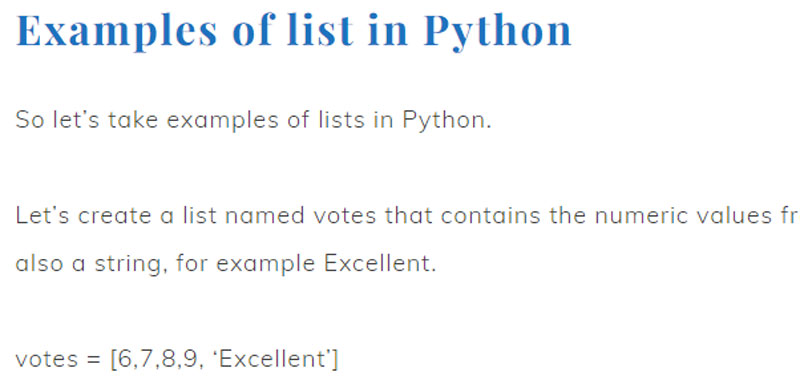
Examples of list in Python
So let’s take examples of lists in Python.
Let’s create a list named votes that contains the numeric values from 6 to 9 and also a string, for example Excellent.
votes = [6,7,8,9, ‘Excellent’]
So, as mentioned before, the values can be of different types.
Let’s take another example of a list that contains values of the same type.
So let’s create a list called seasons, in which we memorize the seasons of the year.
Then we print the list with the print function.
seasons = [‘Spring’, ‘Summer’, ‘Autumn’, ‘Winter’]
print (seasons)
It will print: [‘Spring’, ‘Summer’, ‘Autumn’, ‘Winter’]
Index of the list in Python
As we have already said, each element of the list is assigned an index that starts from the left and starts from 0. So, to print for example the first element we write:
print (seasons [0])
While to print the last element we write:
print (seasons [3])
As we have seen with strings, also with lists we can extract a set of values, that is a sublist:
print (seasons [: 2])
This output will only display the first two items in the list.
Editing list elements in Python
The elements of the list can also be modified by reassigning them a new value.
For example, we assign the value ‘Summer’ to the first element, while the value ‘Spring’ is assigned to the second.
seasons [0] = ‘Summer’
seasons [1] = ‘Spring’
In this simple example I have changed the first and second seasons.
Conclusion
In this lesson we introduced the concept of list in Python, in the next we will talk about the length of a list.
Some useful links
How to find the maximum of N numbers