JavaScript isNaN function determines whether the value passed as an argument is not a number.
The syntax is therefore the following: isNaN(value).
The function returns a Boolean value that is true if the argument passed is not a number, otherwise it returns false.
JavaScript isNaN – examples
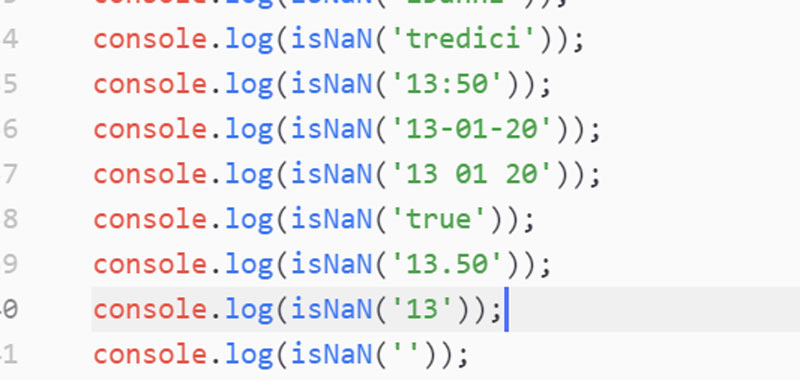
In all the examples presented under the isNaN function gives true:
isNaN('13years');
isNaN('thirteen');
isNaN('13:50');
isNaN('13-01-20');
isNaN('13 01 20');
isNaN('true');
Instead in these other cases it has false value:
isNaN('13.50');
isNaN('13');
isNaN('');
As we can see therefore even if I pass the empty string it gives false as a result, as if it were a number.
Furthermore, even if we pass a number as a string, it always returns false, as in the example below:
var num = '13';
console.log(isNaN(num));
In the browser console we will display false, because the variable num is interpreted as a number.
Some useful links
Introduction to JavaScript language
Learn JavaScript – basic concepts