Fibonacci sequence in Python can have different implementation algorithms.
Recall that the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence of positive integers in which each number starting from the third is the sum of the previous two except the first two which are 1, 1.
For example, if N = 9, the terms of the sequence are: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34.
Fibonacci sequence in Python algorithm
So let’s create an algorithm that represents the Fibonacci sequence.
Take a number N as input and display the N terms of the Fibonacci sequence.
To implement this algorithm, first of all we take two variables a and b and assign the value 1 to both. We thus create the first two terms of the Fibonacci sequence that we will immediately print.
Then, we make a for loop to display the N terms with an index i ranging from 0 to N-1. After, within the cycle we calculate the third term c and then exchange a with b and b with c. Finally we print c.
Here is a possible solution:
n = int(input('How many numbers?: ' ))
a,b = 1,1
print(a)
print(b)
for i in range(n):
c = a+b
a = b
b = c
print(c, end=' ')
Once we understand the procedure, we rewrite the algorithm in a more elegant way, avoiding some instructions, such as the initial prints, and we carry out the exchange in a single line.
Here is the solution:
n = int(input('How many numbers?: ' ))
a,b = 1,1
for i in range(n):
print(a, end=' ')
a,b = b,a+b
print()
Fibonacci sequence in Python algorithm – with a function
We can also use a function to solve the algorithm.
def print_fibonacci(length):
a = 1
b = 1
for i in range (length):
print(a, end=" ")
a,b=b,a+b
n = int(input('How many numbers?: ' ))
print_fibonacci(n)
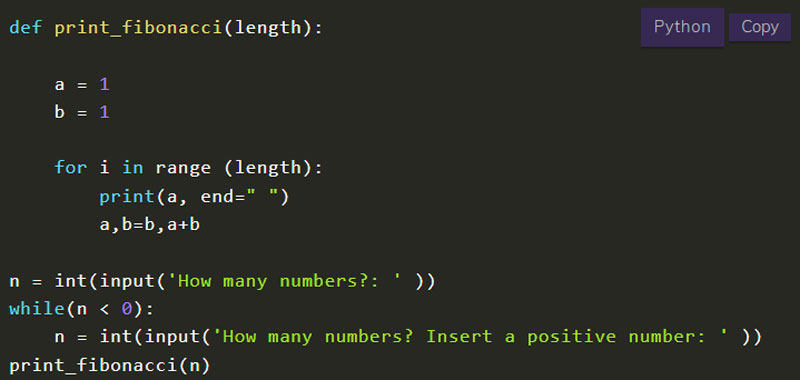
We can also add a control input. If a user insert a negative number the program can be request a new number.
def print_fibonacci(length):
a = 1
b = 1
for i in range (length):
print(a, end=" ")
a,b=b,a+b
n = int(input('How many numbers?: ' ))
while(n < 0):
n = int(input('How many numbers? Insert a positive number: ' ))
print_fibonacci(n)
Fibonacci sequence in Python algorithm – recursive solution
Here is the recursive solution to the algorithm. Remember that recursion is when you have a call directly to the function itself. In our case, in fact, we call the function rec_fib within the same function rec_fib.
def rec_fib(n):
if n > 1:
return rec_fib(n-1) + rec_fib(n-2)
return n
n = int(input('How many numbers?: ' ))
for i in range(1,n+1):
print(rec_fib(i))
Conclusion
In this lesson we studied how to develop a Fibonacci sequence algorithm in Python, in the next lesson we will see how to understand if a number is part of the sequence.